What is Complementary Feeding?

Breastfeeding alone is enough for the first 6 months of a baby’s life. After that, it’s essential to start complementary feeding along with breast milk to support your child’s growth and development. Complementary feeding means introducing semi-solid foods suitable for your baby at the right age.
When to Start Complementary Feeding?
Begin complementary feeding right after your baby turns 6 months old. This is when their digestive system is ready for solid foods, and their ability to chew and swallow starts to develop. Introducing solids at this time helps prevent issues with chewing and eating later on.
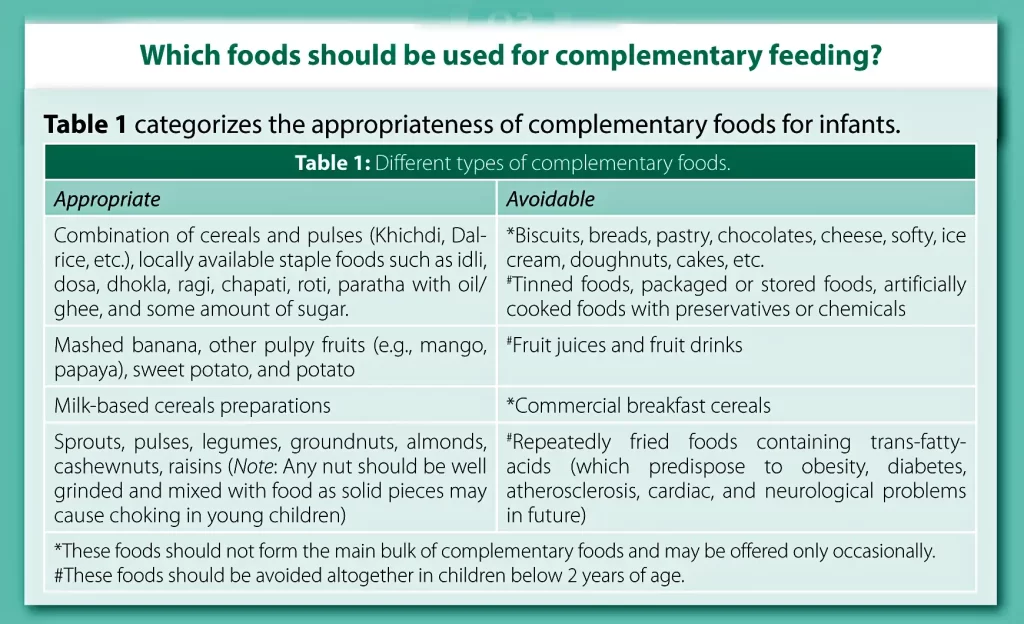
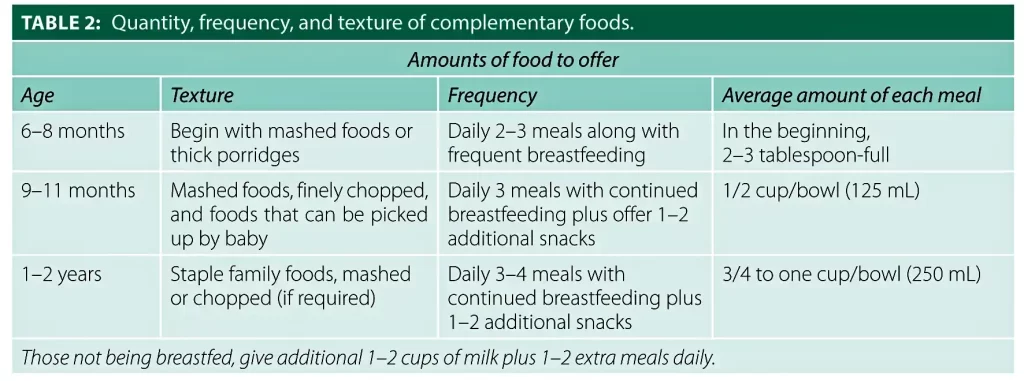
Which Foods to Use for Complementary Feeding?
- Staple Foods: Start with common family foods like rice, wheat, pulses, and vegetables. Use locally available, affordable ingredients.
- Consistency: Begin with pureed or mashed foods and gradually move to thicker, lumpier textures as your child grows.
- Variety: Offer a mix of nutrient-rich foods to ensure a balanced diet.
- Safety: Always prepare food in a clean environment and avoid bottle-feeding to reduce the risk of infections.
How to Ensure Food is Nutritious?
- Respect Preferences: Introduce one food at a time and respect your child’s likes and dislikes.
- Avoid Distractions: Don’t feed your child while watching TV or using a mobile device.
- No Force-Feeding: Make feeding a positive experience, not a forced one.
Things to Avoid:
- Delay in Starting Complementary Feeding: Don’t wait too long to introduce solid foods.
- Junk Food: Avoid processed and packaged foods, as well as foods high in sugar, salt, or unhealthy fats.
- Choking Hazards: Be careful with foods that can easily get stuck in the windpipe, like nuts or grapes.
By following these simple guidelines, you can ensure that your child receives the nutrition they need for healthy growth and development.
